Published: 1981 | Digest of the 3rd CMBFS Canadian Clinical Engineering Conference
Winter humidities and related absenteeism in Canadian hospitals
Green G.
Abstract
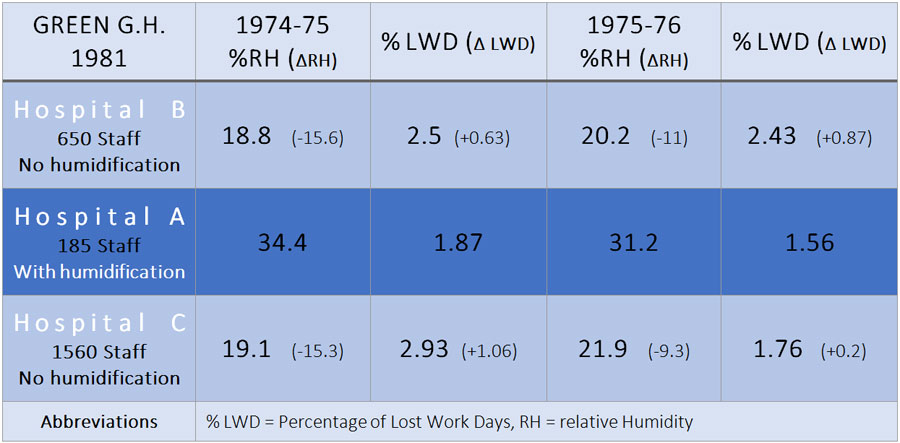
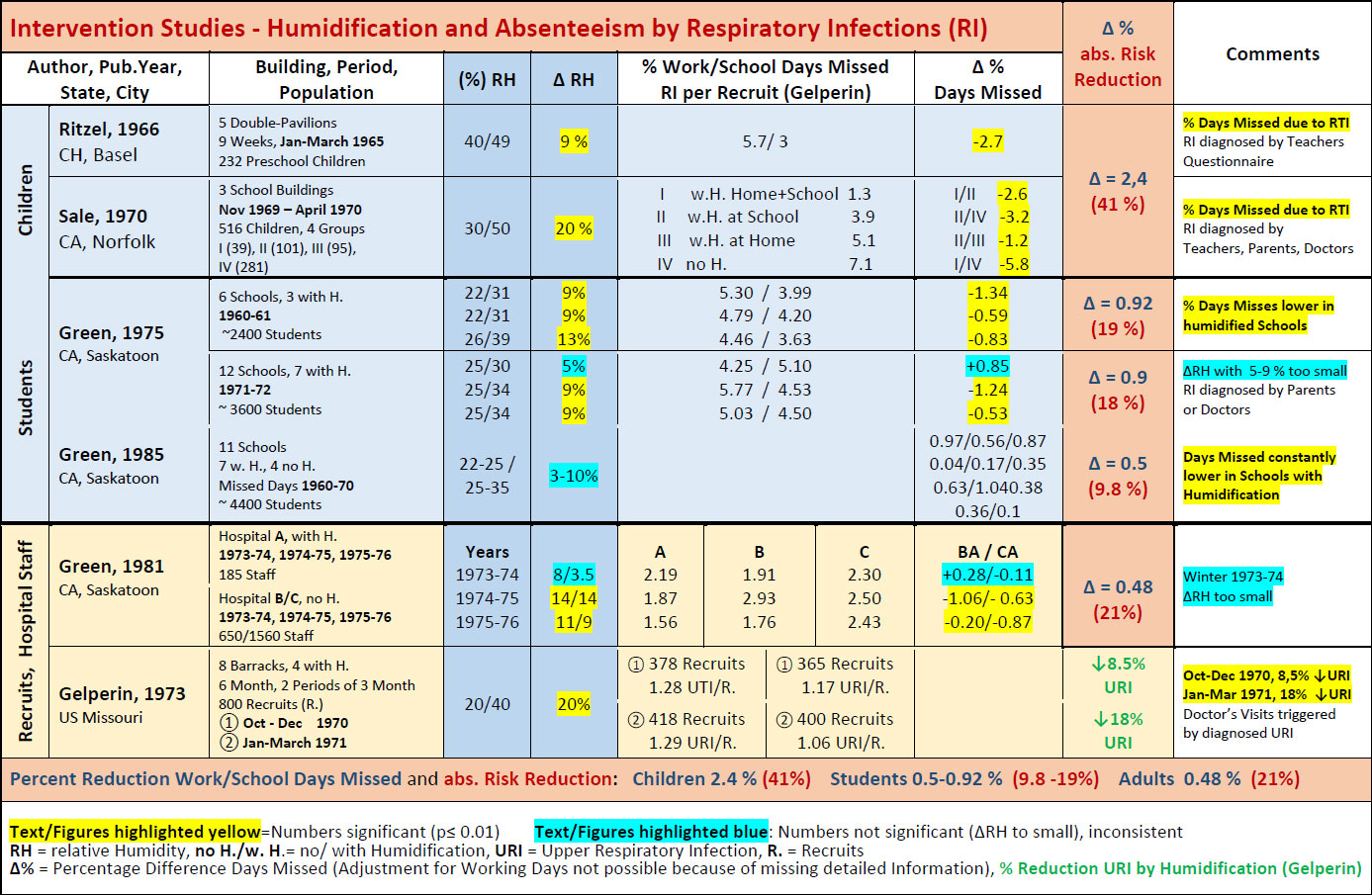
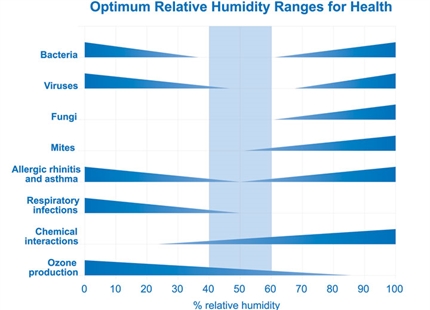
In this study, total staff absenteeism (Lost Work Days - LWD) across three hospitals was compared alongside the average relative humidity of the indoor working environments. The study took place across three winters: 1973/4, 1974/5 and 1975/6. Two of the hospitals had no humidity control (B & C) and one hospital had a humidification system installed (A).
The survey was done across three winter periods (Oct-Apr). Data from winter 1973/74 is not shown in the table, as humidity differences were too small between humidified and non-humidified hospitals, and therefore no difference in absenteeism was detectable. Temperatures in all hospitals were identical, 24°C ±0.5°C.
The table presents the comparison for the two years with significant differences in humidity and LWD’s. The year-long average of LWD is 2.5%. This average workday loss was reduced in the humidified hospital to 1.87% (minus 0.63%) in the winter of 1974/5 and 1.56% (minus 0.94%) in 1975/6.
Absenteeism caused by respiratory illness accounted for roughly 60% of absenteeism, according to an inquiry of hospital staff by the author.